Touch panel technologies include resistive, capacitive, infrared, optical imaging, surface acoustic wave, and electromagnetic induction types. These panels are now very important in devices people use every day. They are also used in many different industries. The global touch panel computer market is growing quickly. It may be worth $38.7 billion by 2032. From 2020 to 2025, industries like automotive, healthcare, and retail have used more touch panels. By 2025, over half of new cars will have touch displays. Picking the right touch panel can make user experience better. It can also help with efficiency and safety.
Touch Panel Overview
Touch panels are very important in 2025. People use them in phones, tablets, and laptops. Car companies put touchscreens in dashboards and controls. Hospitals use touch panels for patient care and medical tools. Factories use them to run machines and watch production. Stores, schools, and hotels use touch panels every day. More smart devices and systems mean we need better touch panels. Companies want panels that work well everywhere. They need to work outside in sunlight and inside clean hospital rooms.
Key Features
Touch panels in 2025 have many new features and parts. These help them work for many people and jobs.
-
Antibacterial coatings and waterproofing make them last longer. This is good for hospitals and food places.
-
Borderless designs make screens look bigger and cooler.
-
Micro-LED and E-Ink save energy and lower costs.
-
5G and IoT let panels share data fast and help with automation.
-
Simple interfaces make them easy to use in factories.
-
Main parts are a touch sensor, controller IC, and software driver.
-
Capacitive panels let you use gestures like pinch and swipe.
-
New panels use in-cell touch, flexible, and very thin sensors.
|
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Can be changed for clear, sharp pictures. |
|
|
Pixel Pitch Flexibility |
Can adjust for different ways to see. |
|
Brightness |
Very bright so you can see in any light. |
|
Energy Efficiency |
Uses less power to save money. |
|
Interactive Capabilities |
Lets you touch and use interactive features. |
|
Size Customization |
Can fit many places and uses. |
|
Durability |
Made to last even in hard conditions. |
|
Maintenance |
Easy and cheap to take care of for a long time. |
What is a touch panel?

A touch panel lets people use a screen by touching it. It sits on top of a display like an LCD or OLED. The panel can tell when someone touches it. You do not need a mouse or keyboard to use it. You can tap, swipe, or drag with your finger or a stylus.
Touch panels work by sensing touch in different ways. A capacitive touch panel has a glass layer with a clear coating. It senses changes in electric charge when you touch it. A resistive touch panel has layers that press together when touched. These methods help the panel know where and how you touch.
Note: Touch panels are input parts, not output parts. They sense touch and send signals to the device. The display shows pictures and information.
Touch panels are different from other input devices. You control things right on the screen. A mouse or touchpad needs a separate surface. A touch panel puts control on the display. This makes using devices faster and easier for many people.
Some important things about touch panels:
-
They sense touch with special layers and materials.
-
You can touch, swipe, or pinch to use them.
-
They work with fingers, styluses, or gloves, depending on the type.
-
Touch panels make devices easier to use in places like phones, cars, and hospitals.
Touch panels have changed how people use technology. They make devices more fun and simple to use. In 2025, touch panels are still very important in daily life and work.
Types of Touch Panel
Resistive
Resistive panels have two thin layers with a gap. When you press the screen, the layers touch each other. This changes the resistance. The system checks this change to find where you touched. You can use gloves, a stylus, or any object.
-
These panels cost less for many uses.
-
You can use them with gloves or styluses.
-
They work well in tough places.
Disadvantages:
-
They only let you touch one spot at a time.
-
The screen is not as clear as other types.
-
They wear out faster if used a lot.
Typical Use Cases:
-
People use them in machines at work.
-
They are in outdoor kiosks.
-
Medical devices use them.
-
ATMs and ticket machines have them.
Tip: Resistive panels are good for places where people wear gloves or need a strong, cheap screen.
Surface Capacitive
Surface capacitive panels have a glass layer with a clear coating. When you touch the screen with your finger, it changes the electric field. The system senses this and finds where you touched. These panels only work with bare fingers or special styluses.
|
Feature |
Surface Capacitive |
Projected Capacitive |
|---|---|---|
|
Durability |
Moderate |
High |
|
Touch Capability |
||
|
Clarity |
High |
High |
|
Best Use |
ATMs, kiosks |
Phones, tablets |
Surface capacitive panels last longer than resistive ones. They are clear and accurate for single touches. But they do not let you use more than one finger. They are not as tough as projected capacitive screens.
Projected Capacitive
Projected capacitive panels have a grid of electrodes under glass. When you touch the screen, it changes the electric charge. The system finds where you touched. These panels let you use many fingers at once. You can pinch, zoom, or swipe.
Key Benefits:
-
They are very strong and do not scratch easily.
-
The screen is bright and clear.
-
They respond quickly and smoothly.
-
You can use them with gloves or when wet.
-
They let you touch with many fingers at once.
Common Uses:
-
People use them in smartphones and tablets.
-
Car dashboards have them.
-
Retail kiosks use them.
-
Medical and work equipment use them too.
Note: Projected capacitive panels are the top choice for consumer devices in 2025. They are strong, clear, and let you use many fingers.
Infrared
Infrared panels use invisible light beams across the screen. Sensors on the edges watch for breaks in the light. When you block the light, the system knows where you touched. You do not have to touch the screen directly.
Advantages:
-
You can use fingers, gloves, or styluses.
-
Dirt or water on the screen does not stop them.
-
They are good for big screens.
Disadvantages:
-
The picture is not as sharp as other types.
-
Bright sunlight can make them not work well.
Typical Use Cases:
-
Interactive whiteboards use them.
-
Outdoor kiosks have them.
-
Retail displays use them.
-
Public info boards use them too.
Optical Imaging
Optical imaging panels use cameras or sensors to see touches. They look for changes in light or shadows on the screen. This works well for big screens and many input types.
|
Feature |
Optical Imaging Panels |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
Light Transmittance |
Excellent |
High clarity and brightness |
|
Gloved Touch |
Excellent |
Works with gloves |
|
Stylus Touch |
Good |
Material-dependent |
|
Durability |
Excellent |
Robust for large displays |
|
Cost |
High |
More expensive |
These panels are best for big screens in public places. They work with fingers, gloves, and some styluses. But water drops or bugs can sometimes cause wrong touches.
Surface Acoustic Wave
Surface acoustic wave panels send sound waves across the glass. When you touch the screen, it stops the waves. The system senses this and finds where you touched.
Benefits:
-
The screen is very clear and looks great.
-
It is sensitive and accurate.
-
The glass is strong.
-
You can use fingers, gloves, or styluses.
Limitations:
-
The screen must be clean.
-
Dust or water can make it not work well.
-
They cost more.
Best Uses:
-
Factories use them for controls.
-
Medical devices have them.
-
Public info displays use them.
-
Cars use them too.
Tip: SAW panels are best for places that need clear pictures and strong screens, like hospitals and factories.
Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction panels use a special pen called a stylus. The pen makes a magnetic field. The screen senses this and tracks the pen. You do not need to touch the screen with your finger.
Typical Use Cases:
-
Car controls and dashboards use them.
-
Machines at work have them.
-
Fancy kitchen appliances use them.
-
Medical equipment uses them.
-
Outdoor kiosks and wearables have them.
These panels work through metal or plastic covers. They resist dust, water, and hot or cold weather. They are very accurate and last a long time.
Note: Electromagnetic induction panels are great for jobs that need to be exact, strong, and work in hard places.
How Touch Panel Works

Working Principles
Every type of touch panel senses touch in its own way.
-
Resistive panels have two thin layers inside. When you press the screen, the layers meet. The system checks this and finds where you touched.
-
Capacitive panels use glass with a special layer. When your finger touches, it changes the electric field. The controller finds this change and marks the spot.
-
Projected capacitive panels have a grid under the glass. When your finger gets close, it changes the field. The system scans the grid to find your touch. These panels can sense more than one finger at once.
-
Infrared panels shine invisible light beams across the screen. If your finger or something else blocks the light, sensors notice and show where you touched.
-
Optical imaging panels use cameras or sensors to watch the screen. When something touches, the system sees the change in light or shadow and finds the spot.
-
Surface acoustic wave panels send sound waves over the glass. When you touch the screen, the waves stop. The system senses where the waves stopped.
-
Electromagnetic induction panels need a special pen. The pen makes a magnetic field. The screen senses this field and follows the pen’s movement.
Tip: Projected capacitive panels use strong glass and let you use many fingers. This makes them a top pick for phones and tablets.
Pros and Cons
The table below shows the main good and bad points for each touch panel type:
|
Type |
Pros |
Cons |
Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Resistive |
Cheap, works with gloves or stylus |
Not as clear, wears out faster |
ATMs, medical devices, kiosks |
|
Capacitive |
Very clear, strong, multi-touch |
Costs more, not great with gloves |
Smartphones, tablets, displays |
|
Projected Capacitive |
Super clear, tough, multi-touch |
Expensive, not as good with thick gloves |
Phones, cars, retail kiosks |
|
Infrared |
Accurate, works with anything |
Sunlight can mess it up, less sharp picture |
Whiteboards, outdoor kiosks |
|
Optical Imaging |
Sensitive, strong, good for big screens |
Glare can be a problem, costs more |
Public displays, info boards |
|
Surface Acoustic Wave |
Clear picture, scratch resistant |
Dirt or water can cause problems, pricey |
Factories, hospitals, info screens |
|
Electromagnetic Induction |
Very exact, works in tough places |
Needs a special pen, costs more |
Medical, industrial, outdoor use |
Note: Picking the best touch panel depends on where and how it will be used. Some types are better for hard places, while others look clearer or let you use more fingers.
Touch Panel Applications

Consumer Electronics
People use touch panels in phones, tablets, and laptops every day. Most of these devices have capacitive touch screens. These screens are very clear and bright. They react fast to light touches. You can use more than one finger at a time. Pinching and zooming are easy to do. Swiping, tapping, and scrolling feel smooth. The screens do not scratch easily. They still work if there is dust or oil on them. Capacitive technology makes using devices simple and fun. People like these screens because they are quick and accurate.
-
Devices:
-
Smartphones
-
Tablets
-
Laptops
-
-
Preferred technology: Capacitive touch screens
Tip: Capacitive touch screens make using electronics easier and more enjoyable.
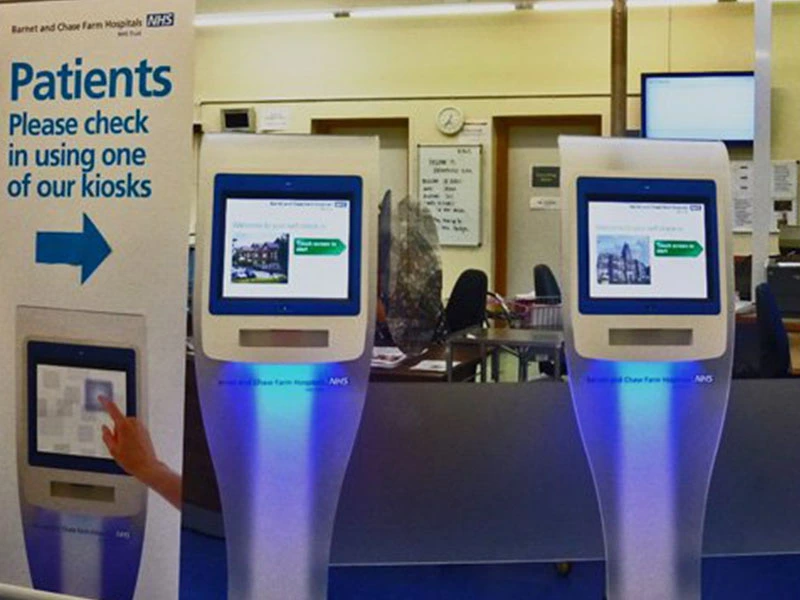
Industrial and Public Use
Factories, hospitals, and public places use touch panels for many jobs. In factories, touch panels help people control machines. Workers use them to watch how things are made. These panels connect to smart systems for fast data and automation. In public, you see touch panels in kiosks and ticket machines. They are also in smart buses and trains. These panels must be strong and easy to clean. They need to work with gloves too. Haptic feedback and scratch resistance help them last longer.
-
Common uses:
-
Medical devices
-
Self-service kiosks
-
Public transportation info screens
-
Technologies: Capacitive, resistive, and infrared touch panels
Note: Industrial touch panels are made tough to handle dust, water, and heat or cold.
Large Displays and Special Uses
Big touch screens in public and special places have special needs. These panels must be bright and strong. They should be easy to see in sunlight. Factories and outdoor areas use panels with hard glass and coatings that stop glare. Some panels use optical bonding to make the screen clearer. Modular designs let panels fit many shapes and sizes. Hospitals and the military need panels that block water, dust, and hits. Custom hardware and software help with special jobs.
-
Applications:
-
Outdoor digital signs
-
Factory control rooms
-
Hospital equipment
-
Military and transportation systems
-
-
Technologies: Infrared, optical imaging, projected capacitive, and resistive touch panels
Callout: Special coatings and strong glass help big touch panels work well in hard places.
Comparison and Selection
Feature Table
The table below shows how the main touch panels are different. It lists their features, what they do well, what they do not, and where people use them most.
|
Feature |
Capacitive Touch Screen |
Resistive Touch Screen |
|---|---|---|
|
Sensitivity |
High |
Moderate |
|
Multi-Touch Support |
Yes |
No |
|
Input Method |
Finger |
Finger or Stylus |
|
Cost |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Durability |
Moderate |
High |
|
Outdoor Performance |
Good |
Needs Anti-Glare Treatment |
|
Industrial Suitability |
Needs Protection |
Highly Suitable |
|
Typical Applications |
Phones, tablets, kiosks |
ATMs, factories, medical devices |
Tip: Capacitive screens are great for fast and smooth touch. They let you use more than one finger. Resistive screens are better for hard jobs and when people wear gloves.
Choosing the Right Type
Picking the best touch panel depends on how and where it will be used. Here are some things to think about:
-
Choose a panel that fits the job. Phones and tablets need to be very sensitive and let you use many fingers. Factories and hospitals need panels that work with gloves and last a long time.
-
See if the panel needs to handle water, dust, or sunlight. Outdoor and factory panels must be strong and tough.
-
Think about who will use it. Some panels only work with fingers. Others let you use a stylus or gloves.
-
Look at price and how good it is. Capacitive panels cost more but feel nicer to use. Resistive panels are cheaper and work well in rough places.
-
Make sure the panel fits the size and shape of the device. Some panels are better for big screens.
-
Think about new things like haptic feedback, gesture control, or voice commands for the future.
Note: In 2025, many companies want panels with smart features like AI, low power use, and easy cleaning. The best panel is one that works well, does not cost too much, and meets what users need.
Every touch panel type is good for different uses in 2025. Capacitive panels are best for phones and tablets. Resistive panels are better for hard work in factories or hospitals. New trends are flexible screens, AI features, and better gesture control. People should pick the right panel for their needs. They should also think about where it will be used. It is smart to plan for upgrades in the future. The table below shows important trends for the next five years:
|
Trend |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Flexible Screens |
Wearables, foldable devices |
|
Smarter, context-aware touch functions |
|
|
Eco-Friendly Design |
Sustainable materials, energy efficiency |
|
AR/VR Compatibility |
Enhanced interactive experiences |
Tip: Picking the right touch panel helps devices last longer. It also makes them work better as technology changes.
Touch Panel FAQ
What is the most common touch panel in smartphones in 2025?
Most smartphones in 2025 use projected capacitive touch panels. These panels let you use more than one finger at once. They react fast and show pictures that look sharp. You can swipe, pinch, or zoom easily on these screens.
Can touch panels work with gloves?
Some touch panels work when you wear gloves. Resistive panels and some projected capacitive panels do this. Many hospitals and factories use these panels for safety. It makes things easier for workers and doctors.
How do touch panels handle water or dust?
Many touch panels have special coatings or seals. These help keep out water and dust. Outdoor and factory panels often use these features. This helps them last longer and work better.
Are touch panels safe for hospital use?
Yes, touch panels are safe for hospitals. They have surfaces that are easy to clean. Some have antibacterial coatings to stop germs. These panels help keep patients safe.
What makes a touch panel last longer?
Touch panels last longer if made with strong glass and good coatings. Cleaning them often and using them the right way helps too. This keeps them working for a long time.

Penny
Web Content Writer
4 years of experience
This article is edited by Penny, the website content writer of COMPT, who has 4 years working experience in the industrial PCs industry and often discusses with colleagues in R&D, marketing and production departments about the professional knowledge and application of industrial controllers, and has a deep understanding of the industry and products.
Please feel free to contact me to discuss more about industrial controllers. sales@gdcompt.com