How to Choose Between Single-Board Computers (SBCs) and Industrial Motherboards in Embedded Systems and Industrial Automation Projects? What Are Their Technical Features and Applicable Scenarios?
I’m Penny from COMPT, with years of hands-on experience in industrial computing hardware. In this article, I’ll combine our industry insights to provide a comprehensive analysis of the core differences between these two types of hardware—from basic definitions and performance comparisons to practical selection advice—helping you make informed decisions based on your project requirements.
Whether you prioritize cost-effectiveness, expandability, or stability in harsh environments, you’ll find COMPT-verified technical analysis and practical purchasing guidance here. Let us help you match the most suitable hardware solution from a professional perspective.
What is a Single Board Computer (SBC)?
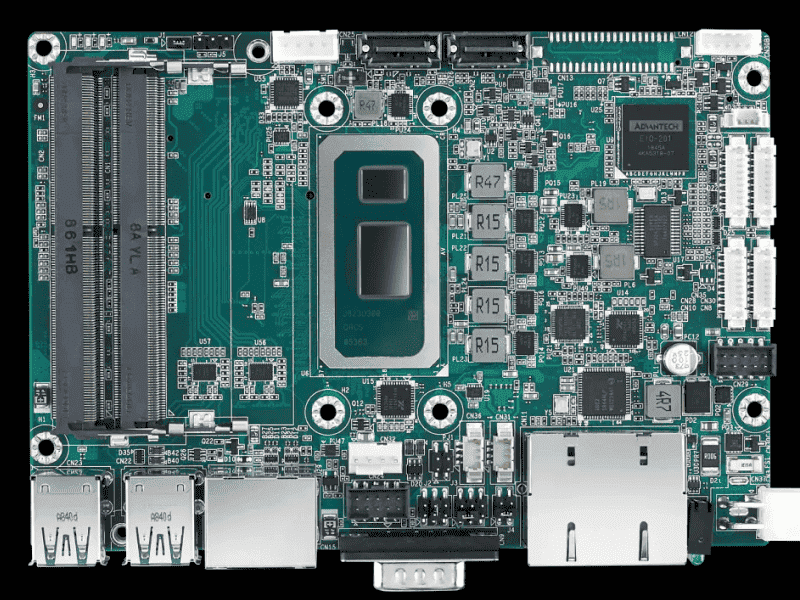
A Single-Board Computer (SBC) is a complete computer system built on a single circuit board, integrating key components like the CPU, memory, storage, and I/O interfaces—eliminating the need for separate parts like a traditional desktop PC. Compact yet powerful, SBCs are designed for efficiency, offering low power consumption, high integration, and cost-effectiveness. Popular examples include the Raspberry Pi, Banana Pi, and BeagleBone, which are widely used in education, IoT, robotics, smart home devices, and industrial automation. Thanks to their small size and versatility, SBCs are ideal for embedded systems, prototyping, and applications where space and energy efficiency matter.
What Is an Industrial Motherboard?
An industrial motherboard (also called an industrial PC motherboard or Industrial Motherboard) is a computer motherboard specifically designed for harsh environments like industrial automation, robotics, medical equipment, and transportation systems. Unlike consumer-grade motherboards, industrial versions prioritize long-term reliability, extreme durability, and stable performance in demanding conditions.
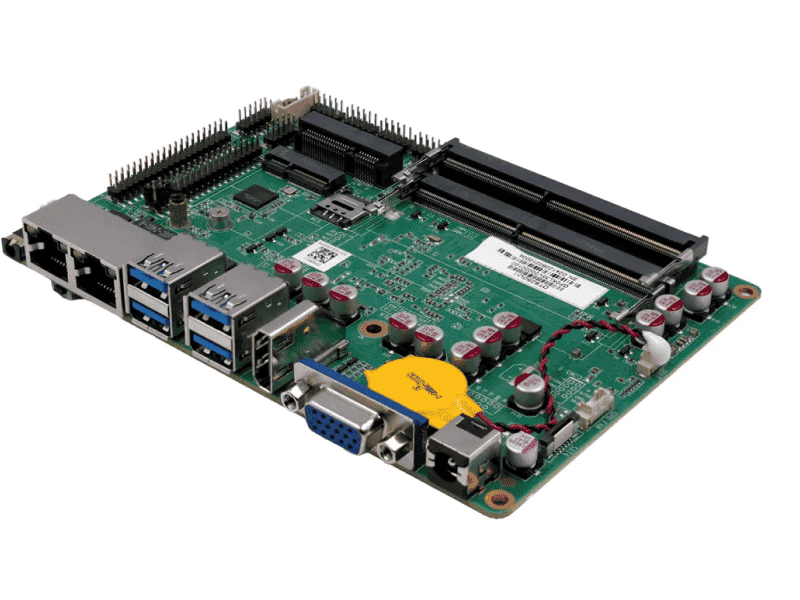
Key Features & Benefits:
-
Built for harsh environments – Operates in extreme temperatures (-40°C to 85°C), high humidity (0-95% non-condensing), and resists dust, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference.
-
Long lifecycle (5-10+ years) – Manufacturers guarantee extended availability to avoid supply disruptions in critical systems.
-
High reliability – Fanless cooling, redundant power design, and watchdog timers ensure 24/7 stability.
-
Industrial-grade connectivity – Includes RS-232/485, CAN bus, GPIO, PoE, PCI/PCIe expansion, and more for seamless integration.
-
Low power, high efficiency – Uses Intel Atom, ARM Cortex-A, or similar processors for edge computing and real-time OS support.
-
Rigorous certifications – Complies with ISO9001, CE, FCC, RoHS, and undergoes stress tests (thermal cycling, shock, etc.).
Industrial motherboards are ideal for mission-critical applications where failure isn’t an option. They offer customizable designs (connectors, form factors, etc.) and long-term availability, making them a smart choice for factories, outdoor systems, and other challenging environments.
Single Board Computer (SBC) vs. Industrial Motherboard: Key Differences Explained
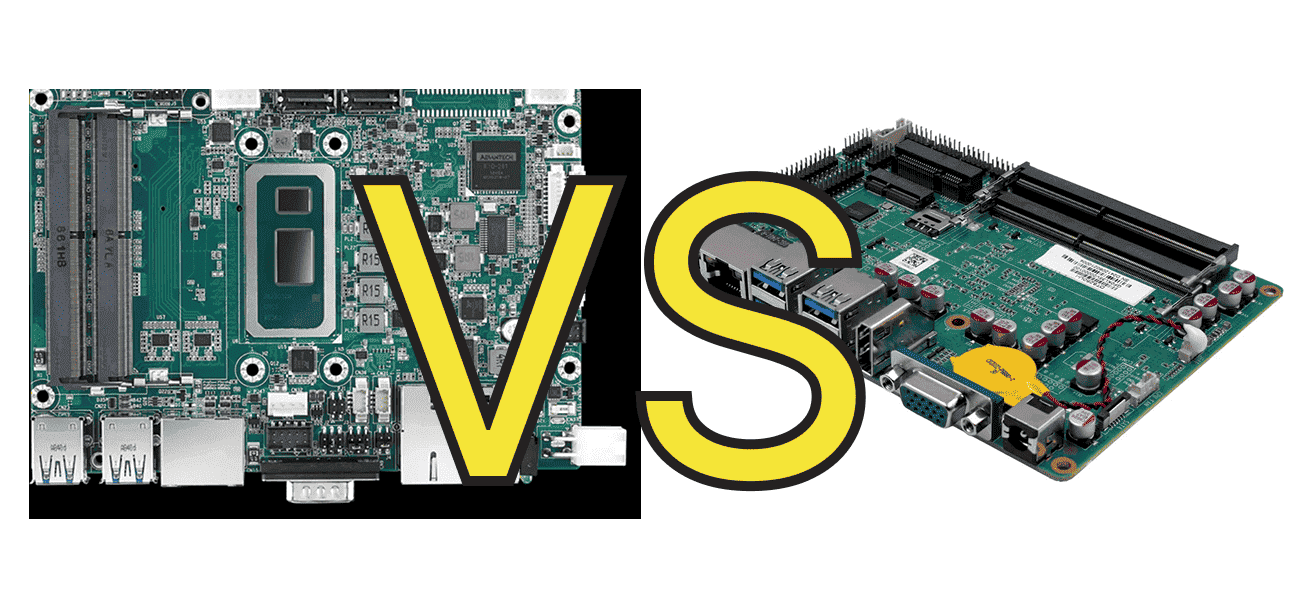
If you’re deciding between a Single-Board Computer (SBC) and an Industrial Motherboard, think of it like choosing between a pocket-sized DIY gadget and a heavy-duty workhorse. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Feature | Single Board Computer (SBC) | Industrial Motherboard |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Cheap (50–300, e.g., Raspberry Pi) | Expensive (200–2000+) |
| Best For | Learning, IoT, smart home, hobby projects | Factories, medical devices, transportation |
| Durability | Indoor use only | Dustproof, shock-resistant, wide temp range (-40°C to 85°C) |
| Expandability | Fixed ports (USB, HDMI) | Slots for add-ons (PCIe, multiple LAN ports) |
| Lifespan | 2–5 years (rapidly evolving) | 5–10 years (long-term supply) |
Which One Should You Choose?
-
Pick an SBC (like Raspberry Pi) if you’re tinkering with coding, building a smart device, or doing small-scale projects. They’re affordable, easy to use, and great for prototyping.
-
Go for an Industrial Motherboard if you need 24/7 reliability in harsh environments (factories, hospitals, outdoor systems). They cost more but won’t fail under pressure.
Application Scenarios of Single Board Computers vs. Industrial Motherboards
Single-board computers (SBCs) and industrial motherboards each play unique roles in different application scenarios. Below are some of their primary use cases:
Application Scenarios of Single-Board Computers
-
IoT Devices: SBCs can serve as the central controller for IoT devices, managing and controlling various sensors, actuators, and other peripherals.
-
Robotics Control: SBCs can act as the main controller for robots, managing their movement and various operations.
-
Personal Media Centers: SBCs can be connected to TVs to function as personal media centers for watching videos, playing music, and more.
-
Electronics Projects: SBCs can serve as controllers for electronics projects, managing peripheral devices and executing various tasks.
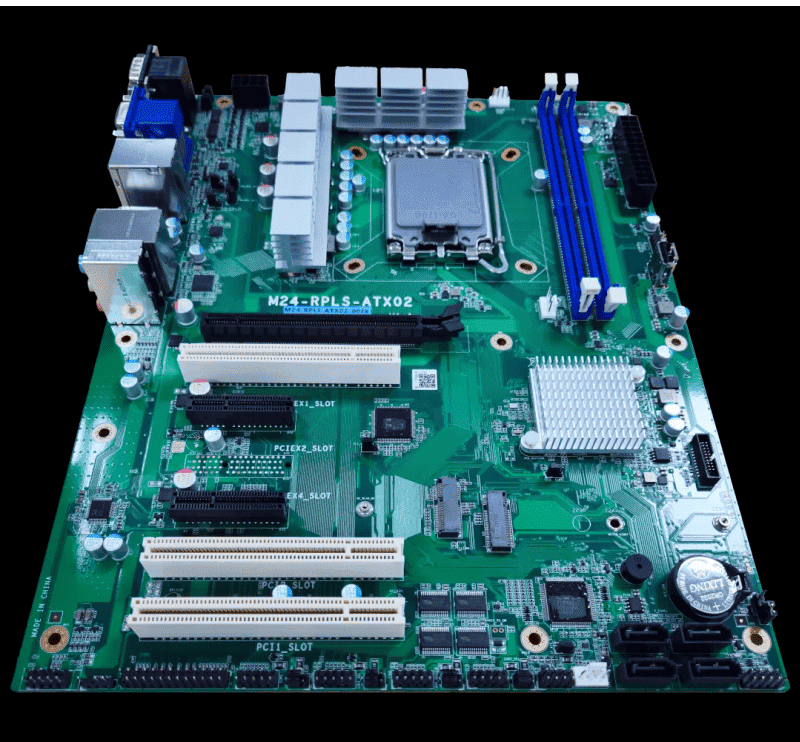
Application Scenarios of Industrial Motherboards
-
Industrial Automation Control: Industrial motherboards can replace PLCs or DCS systems to achieve automated control and monitoring of production processes. In industries such as automotive manufacturing, food processing, textiles, and printing, they are used to manage production line schedules and monitor the quality and safety of each process in real time.
-
Data Acquisition and Processing: Industrial motherboards can collect raw data through various sensors, then process, store, analyze, and visualize the data. In medical equipment, they are used for precise control and data acquisition, such as in surgical robots and pacemakers.
-
Robotics Control: Industrial motherboards can drive and control robots, enabling industrial automation and smart manufacturing. On automated production lines, they work alongside robots to perform tasks like assembly and material handling.
-
Medical Equipment Control: Industrial motherboards play a critical role in controlling medical devices, such as serialized surgical instruments and ventilators. In operating rooms, they integrate with surgical robots to enable precise surgical operations.
-
Traffic System Control: Industrial motherboards can be used to control and monitor traffic management systems, such as traffic light and streetlight control systems. In smart transportation systems, they work with cameras and sensors to monitor traffic flow and manage signal lights.
-
Smart Home Systems: As the core control device in smart homes, industrial motherboards connect various sensors and actuators to enable remote control and intelligent management of home appliances.
Latest Trends in Single-Board Computers (SBCs) vs. Industrial Motherboards
Single-board computers (SBCs) and industrial motherboards are evolving rapidly, but their development paths differ—SBCs focus on flexibility and AI edge computing, while industrial motherboards prioritize industrial-grade stability and high-performance expansion. Here’s a breakdown of their key trends:
1. Latest Trends in Single-Board Computers (SBCs)
✅ AI and Edge Computing Boom
-
Trend: SBCs are becoming “mini AI brains,” integrating NPUs/GPUs to run AI models directly on-device.
-
Examples:
-
NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano (40 TOPS, handles Transformer models).
-
Raspberry Pi AI Kit (paired with Hailo-8L accelerator, low-cost AI solution).
-
-
Use Cases: Real-time object detection (security cameras), smart voice assistants.
✅ Rise of RISC-V (Open-Source & Cost-Effective)
-
Trend: More RISC-V-based SBCs are emerging, avoiding ARM licensing fees—ideal for customization and localization.
-
Examples:
-
BeagleV-Fire (quad-core RISC-V, great for embedded development).
-
SiFive HiFive Unmatched (high-performance RISC-V dev board).
-
✅ Modular Design (Like LEGO for Tech)
-
Trend: Manufacturers offer “compute modules” (e.g., Raspberry Pi CM4), letting users customize carrier boards.
-
Applications: Upgrading industrial equipment (swap just the compute module), custom smart kiosks.
✅ Power Efficiency (Perfect for Solar/IoT)
-
Examples:
-
Rockchip RK3588 (8-core ARM, 8K video decoding, <5W power draw).
-
*ESP32-S3* (Wi-Fi 6 + ultra-low power, ideal for battery-powered devices).
-
2. Latest Trends in Industrial Motherboards
Built for AI and Big Data
-
Upgrades:
-
CPUs: Intel 12th Gen Core/AMD Ryzen Embedded.
-
Storage: NVMe SSDs + DDR5 RAM.
-
-
Use Cases: Factory machine vision, medical imaging.
Powerful Graphics (Essential for Machine Vision)
-
Solutions:
-
Integrated GPUs (e.g., Intel Iris Xe).
-
Support for dedicated GPUs (e.g., NVIDIA RTX A2000).
-
Connectivity King
-
New Tech:
-
Wired: 10GbE, multi-port redundancy.
-
Wireless: Wi-Fi 6/5G modules (easier IoT connectivity).
-
Military-Grade Security
-
Features:
-
Hardware encryption chips (prevents data breaches).
-
Secure boot (blocks malware).
-
Smart Remote Management
-
Capabilities:
-
Remote monitoring (temperature/power usage).
-
Automatic fault diagnosis (reduces downtime).
-
COMPT has always been dedicated to the research, development, and manufacturing of industrial-grade computing equipment. Our range of Panel PCs (industrial touch all-in-one computers) is built on highly reliable industrial motherboards, offering exceptional environmental adaptability and interface expansion capabilities. They are widely used in complex application scenarios such as smart manufacturing, warehousing and logistics, and agricultural equipment.
Contact us to learn about customized Panel PC solutions based on industrial motherboards, helping you build more efficient and stable industrial application systems.
Single Board Computer vs. Industrial Motherboard FAQ
1.Can SBCs be used in industrial environments?
Some can, but industrial-grade models (e.g., Jetson AGX Orin Industrial) are recommended. Regular SBCs (e.g., Raspberry Pi) require reinforcement.
2.Why are industrial motherboards more expensive?
Industrial-grade components, strict certifications (CE/EMC), and long-term supply guarantees (10+ years).
3.SBC or industrial motherboard?
Low cost/rapid development → SBC;
High reliability/harsh environments → Industrial motherboard.
4.Can a Raspberry Pi be used as an industrial PC?
Suitable for short-term temporary use; for long-term, industrial alternatives (e.g., RevPi Core 3) are recommended.
5.Do industrial motherboards support Windows?
x86 architecture: Yes; ARM architecture: Linux/WinRT only.
6.Which will dominate in the AIoT era?
SBCs: Lightweight edge computing;
Industrial motherboards: Complex AI + 5G scenarios.

Penny
Web Content Writer
4 years of experience
This article is edited by Penny, the website content writer of COMPT, who has 4 years working experience in the industrial PCs industry and often discusses with colleagues in R&D, marketing and production departments about the professional knowledge and application of industrial controllers, and has a deep understanding of the industry and products.
Please feel free to contact me to discuss more about industrial controllers. sales@gdcompt.com